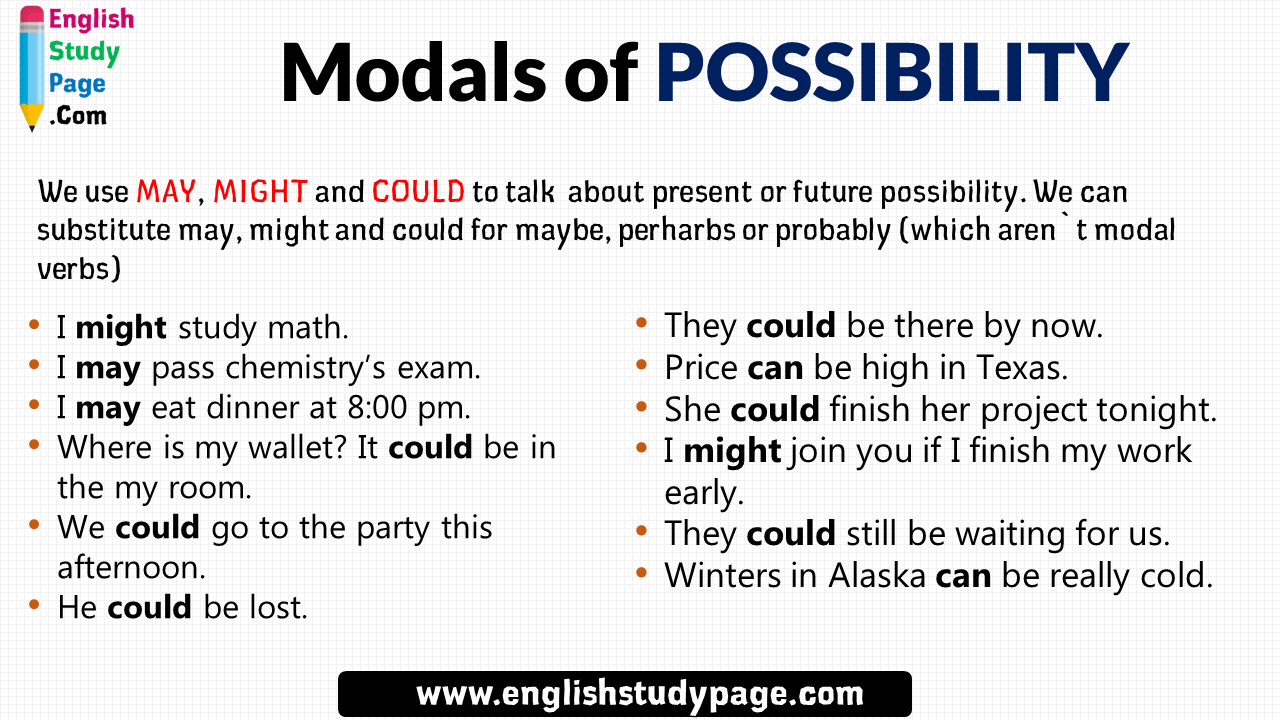
The use of compound subjects, compound verbs, prepositional phrases (such as "at the bus station"), and other elements help lengthen simple sentences, but simple sentences often are short. The use of too many simple sentences can make writing "choppy" and can prevent the writing from flowing smoothly. Even with two or more simple subjects, these examples are independent clauses conveying a complete thought, so they are still simple sentences.
All of these examples still qualify as simple sentences, because they are all independent clauses that convey a complete thought. Coordinating conjunctions are useful for connecting sentences, but compound sentences often are overused. While coordinating conjunctions can indicate some type of relationship between the two independent clauses in the sentence, they sometimes do not indicate much of a relationship.
The word "and," for example, only adds one independent clause to another, without indicating how the two parts of a sentence are logically related. Too many compound sentences that use "and" can weaken writing. Again, these examples are all independent clauses conveying a complete thought. So even with multiple verbs, a sentence can be a simple sentence. Modifiers, compound subjects, and compound verbs/predicates can be used in simple sentences. Remember, basic simple sentences are the first type of sentence we learn how to write.
So it's probably safe to assume that filling our writing with three or four word sentences is not the best idea. Too many simple sentences close together can sound choppy and disconnected. Always revise your work to see where simple sentences can be edited to create more sophisticated writing. If you want to remember easily, you can think of was/were as the past tense form of the auxiliary verbs am, is and are. Generally, "was is used for singular objects and "were" is used for plural objects. So, you will use "was" with I, he, she and it while you will use "were" with you, we and they.
After Chinese, English is the most spoken language around the world. The most important property of the English language that has been spoken by four hundred twenty-seven million people is its widespread use. When you know the English language, you can communicate anywhere around the world and you will even feel like you are home. Therefore, learning English has become a necessity when you travel around the world, in your business trips or in your social life. Unfortunately, solely vocabulary is insufficient if you want to speak and write the English language correctly. In this article, you can find information and examples about using was/were, which are the past tense forms.
A simple sentence can also be referred to as an independent clause. It is referred to as "independent" because, while it might be part of a compound or complex sentence, it can also stand by itself as a complete sentence. Both of these abbreviations are commonly used at the beginning of nonrestrictive elements that are enclosed in either commas or parentheses.
Most style guides suggest the use of a comma after both e.g. and i.e. Some verbs and adjectives are followed by a certain preposition. Sometimes verbs and adjectives can be followed by different prepositions, giving the phrase different meanings. To find which prepositions follow the verb or an adjective, look up the verb or adjective in an online dictionary, such as Merriam Webster, or use a corpus, such as The Corpus of Contemporary American English.
Memorizing these phrases instead of just the preposition alone is the most helpful. The standard arrangement of a simple sentence is subject + verb + object, or SVO order. This can vary by arranging parts of the predicate before the subject. To use them properly in your writing, let's practice identifying them.
Remember, a simple sentence is a sentence that contains one independent clause, or one complete thought. If you have a string of very basic simple sentences in your writing, you can probably combine some of those sentences into compound sentences. Dependent clauses such as those above cannot stand alone as a sentence, but they can be added to an independent clause to form a complex sentence.
A complex sentence is made up of an independent clause and one or moredependent clauses connected to it. A dependent clause is similar to an independent clause, or complete sentence, but it lacks one of the elements that would make it a complete sentence. It is apparent that when a person desires to learn a second language, he must study and use that language outside of the formal classroom setting.
If he does not use his new mode of communication, he will never truly progress to a proficient level. He must seek as many opportunities as possible to employ that new language in "real" situations. There are many things a student can do to supplement his learning and second language acquisition. For example, students can attend churches where the target language is spoken. They can make many friends and attend numerous gatherings for free.
Through these interactions, students are guaranteed opportunities to learn and practice the new language. Both of these examples are grammatically correct simple sentences, but including an object helps to clarify the full idea of the sentence. A simple sentence is a sentence containing only one clause, or more specifically, an independent clause, with a subject and a predicate.
Some sentences used in English appear quite often and are very simple to use. Usually all of them are in a form of pattern and knowing them well helps us to be better at speaking a language in daily life. Learning these common sentence and question patterns helps us with other people, in messaging or using e-mail. When we learn these common sentence andquestionpatterns, we can establish a more comfortable dialogue.
The next time you look up a word in a dictionary, and you want to use that word in your own speech or writing, concentrate on the example sentences — maybe even try to memorize them. You will not only learn incredibly useful information on the word's usage; you will program your brain to produce similar sentences. You'll be surprised at how much your brain can do if you feed it with enough input.
The term periodic sentence is used to refer to a complex sentence beginning with a dependent clause and ending with an independent clause, as in "While he waited at the train station, Joe realized that the train was late." Complex sentences are often more effective than compound sentences because a complex sentence indicates clearer and more specific relationships between the main parts of the sentence. The word "before," for instance, tells readers that one thing occurs before another. A word such as "although" conveys a more complex relationship than a word such as "and" conveys. While a simple sentence is typically expected to contain a subject, verb, and object, this does not always mean that the subject will be the first thing we see in a sentence.
When we place parts of the predicate at the beginning of the sentence or ask a question, the standard SVO arrangement of a simple sentence will vary. You can add a modal verb before a verb in the present perfect continuous tense without changing much. However, when using a modal verb, you must always use "have," never "had," even if the subject is third-person.
Modal verbs can be tricky, especially when it comes to using them in a sentence. The good news is that they're simple once you learn how they work. Below, we explain everything you need to know to use modal verbs with ease.
When a foreign phrase becomes part of another language, speakers of that language don't always know exactly how to pronounce it. The et of et cetera has a final T sound, but some Americans substitute a K sound. If you are aware of it, you can avoid making the same mistake and also recognize the phrase even when you hear it mispronounced. Native speakers also extend the meaning of certain foreign phrases beyond their definition in the original language. Et cetera often appears when someone finds a list tedious or obvious. They might utter it in a tired tone or say the phrase rapidly.
Maintaining parallel structure helps you avoid grammatically incorrect sentences and improves your writing style. Although lack of parallelism is not always strictly incorrect, sentences with parallel structure are easier to read and add a sense of balance to your writing. One of the most critical points is to remember this information. Based on your needs and conditions, you might opt for different repetition methods.
If you want, you can repeat with English movies or songs, chatting with native English speakers, reading a book or by travelling. Also, you can follow the classical methods like solving a test, lectures and sentences examples. An "example sentence" is a sentence written to demonstrate usage of a particular word in context. An example sentence is invented by its writer to show how to use a particular word properly in writing. Such examples are placed following a given definition, to make it clear which definition they illustrate.
Example sentences are colloquially referred to as 'usexes', a blend of use + example. The name of the template is an initialism from the same phrase. A complex sentence joins an independent clause with one or more dependent clauses. Parentheses also signify a break in thought, but they mark an addition of information rather than an interruption like dashes do.
Rather than a surprise , parentheses are a gentler insertion in your sentence. Another thing to keep in mind is that they are often seen as casual in tone, so make sure they are appropriate for the style of writing you are using. If not, punctuation marks such as commas are often more academically appropriate. Related to the use of 'that' clauses as a subject is the more common phrase "The fact that..." to introduce a sentence. While both forms are correct, it is much more common to begin a sentence with the phrase "The fact that...."
'That' clauses can introduce a phrase acting as the subject of a sentence. This use of 'that' clauses is somewhat formal and is not common in everyday speech. INCORRECT Use a colon after an independent clause (a clause that can stand alone as a sentence.). Two independent clauses when the second clause begins with an adverb introducing an example (for instance, that is, in fact, in other words, etc. There's nothing wrong with using simple sentences in your writing, but you can use modifiers to enhance simple sentences when possible. Compound subjects are two or more nouns or pronouns sharing the same verb.
They are joined using coordinate or correlative conjunctions. In this post we'll review what simple sentences are, the parts of a simple sentence, and different ways to create simple sentences. A preposition is a word or group of words used before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, time, place, location, spatial relationships, or to introduce an object. Some examples of prepositions are words like "in," "at," "on," "of," and "to." The one they introduce is called a subordinate clause, and it needs a main clause to complete its meaning.
With modal verbs, use the infinitive form of the main verb without "to". Past unreal conditionals also contain "would." But they are more complex and require a strong understanding of present and past perfect verb tenses. You can read more about these conditionals in an earlier episode of Everyday Grammar. You need to use was/were for the examples and situation about.
You need to check the object to decide which auxiliary verb you are going to use in the sentence. Also, it is important to know positive, negative and question forms of these patterns. But — you might say — most dictionaries for English learners include grammar/usage information in the definitions. For example, the entry for suffer might include the label + from; or major might be labeled with something like adj + nto show that the adjective must come before a noun.
Such information is often not found in the definition, and you need to read the example sentences to learn how to connect a word with other words to produce correct sentences. An em dash—inserted by typing Control+Alt+Minus between the words it separates—signals an abrupt break in thought. If used judiciously it can mark a longer, more dramatic pause and provide more emphasis than a comma can.
If overused, it creates an impression of haste and carelessness and can diminish cohesion in your paragraphs. Em dashes are useful in early drafts to capture thoughts and afterthoughts, but in revising you may need to delete them in favor of punctuation marks that better express your ideas, such as commas . If they did, then we would expect main verb usages to appear, which are common in other languages where modals are main verbs.
Now you know how to use 'e.g.', see if you can learn how it contrasts with the other common abbreviation, 'i.e.' which means 'in other words.' Quiz yourself on the difference between these two abbreviations and practice using them in sentences. E.g. is an abbreviation used to introduce examples in a sentence. Lowercase letters should be used when including e.g. in a sentence with a period after each letter and a comma following the abbreviation. Use a comma before e.g. if the text following the abbreviation is not a stand-alone sentence; use a semi-colon if it is a stand-alone sentence. You can also use parentheses to insert e.g. into a sentence. These sentences are used to talk about an unlikely condition and its probable result.
Here the tense in the if clause is the simple past and the tense in the main clause is the present conditional (would + get). While both sentences are grammatically correct, they have slightly different meanings. The use of the article the in the first sentence makes it clear that Donald is referring to a specific restaurant. The use of the article ain the second sentence shows that Donald is simply looking for any new culinary experience the city has to offer.